The Importance of 2D and 3D Drawing in Mold Design
2024-09-05
Mold design is a critical process in manufacturing, enabling the mass production of parts used in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. One of the key elements of successful mold design is the creation of 2D and 3D drawings, which provide engineers and designers with a visual representation of the mold structure and the final product. These drawings not only guide the mold-making process but also help ensure quality and efficiency in manufacturing. In this blog, we’ll explore the significance of both 2D and 3D drawings in mold design and their roles in the production process.
What Is 2D Drawing in Mold Design?
A 2D drawing is a flat, two-dimensional representation of the mold and its components. It typically includes orthographic views (top, front, and side views) that detail the dimensions, materials, and tolerances of the mold. While 2D drawings are static and simple, they provide precise measurements and specifications necessary for manufacturing.
In mold design, 2D drawings are often used for:
- Communicating dimensions and tolerances: Engineers use 2D drawings to convey exact measurements, ensuring that the mold and final product meet the required specifications.
- Creating manufacturing blueprints: Machinists and toolmakers rely on these drawings to understand the critical dimensions for machining each part of the mold.
- Reviewing quality control: The 2D drawings serve as a reference for inspection, ensuring that the mold parts adhere to the intended design specifications.
Advantages of 2D Drawings
Despite the rise of 3D modeling, 2D drawings remain valuable in mold design for several reasons:
- Simplicity: 2D drawings are easy to interpret and create, making them ideal for communicating basic design elements.
- Precision: Detailed dimensions and annotations in 2D drawings offer accurate representations of each mold component.
- Documentation: 2D drawings are often used as official documents, providing a record of the mold’s design for future reference or revision.
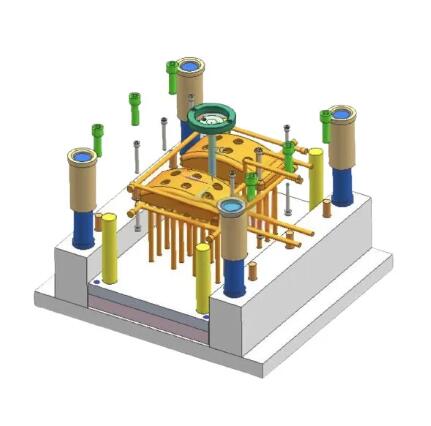
What Is 3D Drawing in Mold Design?
In contrast, a 3D drawing (or 3D model) provides a three-dimensional view of the mold, offering a more realistic and comprehensive visualization of the entire mold assembly. Designers and engineers can rotate and manipulate the model to view it from different angles, gaining deeper insights into the mold’s structure and function. Commonly created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, 3D models enable more advanced design processes compared to traditional 2D drawings.
In mold design, 3D drawings are essential for:
- Complex geometry visualization: For intricate parts and mold designs, 3D models offer a clear representation of curves, contours, and internal structures.
- Interference checks and simulation: With 3D models, designers can simulate the mold’s functionality, checking for any interferences or misalignments before production begins.
- Collaboration and communication: 3D models facilitate collaboration between different departments, such as design, engineering, and manufacturing, by providing a clear and interactive view of the project.
Advantages of 3D Drawings
3D drawings offer several benefits that make them indispensable in modern mold design:
- Realistic visualization: 3D models allow designers to see how the mold will look and function in the real world, reducing the risk of design errors.
- Virtual testing: By using simulation tools, designers can test the mold’s performance in various conditions, identifying potential issues before physical production.
- Efficiency: 3D models streamline the design-to-manufacturing process, as they can be directly used for CNC machining and 3D printing.
The Role of 2D and 3D Drawings in Mold Design
In mold design, both 2D and 3D drawings play complementary roles. While 2D drawings are essential for precise measurements and documentation, 3D models offer a more dynamic and comprehensive view of the design. Together, they provide a complete understanding of the mold’s geometry and function, ensuring that the final product meets quality and performance standards.
For instance, a 2D drawing might include critical dimensions and tolerances for the mold’s components, while a 3D model allows designers to visualize how those components fit together and function during the molding process. By using both 2D and 3D drawings, engineers can ensure accuracy, avoid costly design errors, and optimize the manufacturing process.
Conclusion
The use of both 2D and 3D drawings in mold design is crucial to achieving precision, efficiency, and quality in manufacturing. While 2D drawings remain valuable for documenting specifications and guiding production, 3D models provide the visualization and simulation tools needed to design complex molds. Together, these techniques enable manufacturers to create high-quality products that meet the demands of today’s competitive market.